Can thermal paste damage the motherboard?
Can thermal paste damage the motherboard? It’s a question that often pops up when it comes to computer maintenance. Thermal paste plays a crucial role in keeping our CPUs cool, but can it also pose a risk to our precious motherboards? In this blog post, we’ll explore the potential dangers and precautions associated with thermal paste, ensuring you have all the information you need to avoid any mishaps.
How Does Thermal Paste Work?
Thermal paste is a crucial component when it comes to maintaining optimal temperatures for your computer’s CPU. But how does it actually work?
Thermal Conductivity Properties of Thermal Paste
Thermal paste possesses unique properties that make it an excellent conductor of heat. It is specifically designed to transfer heat efficiently from the CPU to the cooler. This is achieved through its high thermal conductivity, which allows heat to flow from the CPU to the cooler more effectively.
Filling Microscopic Gaps
One of the key purposes of thermal paste is to fill in the microscopic gaps that naturally exist between the CPU and the cooler. These tiny gaps, even though they may seem insignificant, can hinder the efficient transfer of heat. Thermal paste acts as a bridge, filling these gaps and creating direct contact between the CPU and the cooler.
Potential Risks of Using Thermal Paste
When it comes to applying thermal paste, it’s essential to strike the right balance. Using too much or too little can lead to potential risks that could impact the performance and longevity of your computer. Let’s explore these risks and understand why proper application is crucial.
Using Too Much or Too Little Thermal Paste
Applying an excessive amount of thermal paste can be counterproductive. It can create a thick layer between the CPU and the cooler, impeding heat transfer instead of facilitating it. This can result in higher temperatures, reduced cooling efficiency, and potential overheating issues.
On the other hand, using too little thermal paste can lead to insufficient coverage. This means that there may be gaps or uneven distribution, which can hinder the proper transfer of heat. As a result, hotspots may form, leading to increased temperatures and potential damage to the CPU.
Thermal Paste Spillage and Consequences
During the application process, it’s crucial to be cautious and avoid any spillage of thermal paste onto the motherboard. If thermal paste makes contact with the motherboard’s electrical components, it can cause short circuits or damage them. This can lead to malfunctions, system instability, or even permanent damage to the motherboard.
To prevent spillage, it’s recommended to apply thermal paste carefully and precisely, ensuring it only goes where it needs to be – between the CPU and the cooler. Taking your time and using the appropriate amount can significantly reduce the risk of accidental spills.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices
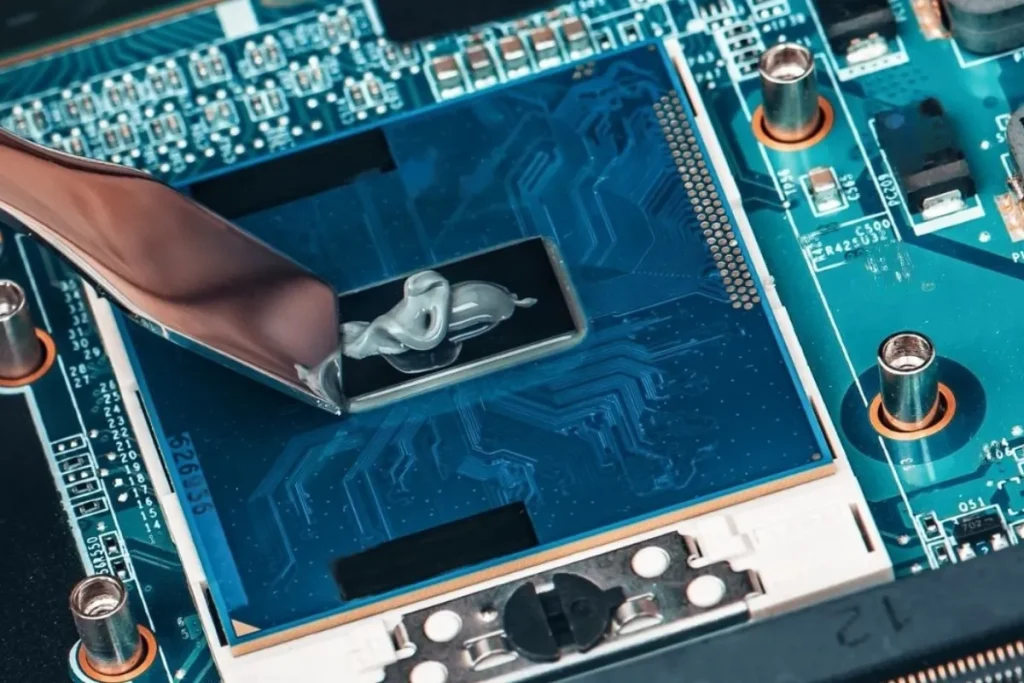
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your CPU, it’s essential to follow preventive measures and best practices when it comes to thermal paste application. step-by-step instructions for applying thermal paste correctly and discuss the importance of cleaning and reapplying it during CPU cooler installation.
Step-by-Step Instructions for Applying Thermal Paste
- Start by preparing the CPU: Power off your computer, disconnect the power supply, and carefully remove the CPU cooler.
- Clean the CPU and cooler: Use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth to clean off any existing thermal paste residue from both the CPU and the cooler. Ensure a clean and dry surface.
- Apply a small amount of thermal paste: Take a pea-sized amount of thermal paste and place it in the center of the CPU. Avoid using too much, as it can lead to excessive spreading and potential risks.
- Spread the thermal paste: Gently place the CPU cooler on top of the thermal paste. Apply even pressure and allow the cooler’s weight to spread the paste naturally. Avoid twisting or sliding the cooler, as this can cause uneven distribution.
Importance of Cleaning and Reapplying Thermal Paste
During CPU cooler installation or when upgrading your computer, it’s crucial to clean off the old thermal paste and reapply a fresh layer. Over time, the thermal paste can dry out, lose its effectiveness, and hinder heat transfer.
Cleaning and reapplying the thermal paste ensures a clean surface and optimal contact between the CPU and the cooler. This promotes efficient heat dissipation and helps maintain lower temperatures, ultimately enhancing the performance and lifespan of your CPU.
Alternative Cooling Solutions
While the thermal paste is the most commonly used method for CPU cooling, there are alternative solutions available that offer different benefits and considerations. Let’s briefly explore these alternatives, including liquid cooling and thermal pads, and discuss their pros and cons compared to thermal paste.
Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling systems, also known as water cooling, use a pump and radiator to dissipate heat from the CPU. This method offers more efficient cooling compared to traditional air cooling, as the liquid can transfer heat more effectively. Liquid cooling systems are often favored by overclockers or individuals seeking maximum cooling performance.
Pros:
- Excellent heat dissipation, allowing for lower CPU temperatures.
- Can handle heavy overclocking and high-performance systems.
- Generally quieter than air cooling solutions.
Cons:
- More complex installation process compared to air cooling.
- Higher cost due to additional components and maintenance requirements.
- Potential risks of leaks or pump failures can damage components.
Thermal Pads
Thermal pads are another alternative to thermal paste. These are pre-cut pads made of a thermally conductive material that is placed between the CPU and cooler. They offer a convenient and mess-free solution for thermal management.
Pros:
- Easy to apply and remove without the need for cleaning.
- Can provide consistent thermal conductivity without the risk of improper application.
- Suitable for situations where re-application of thermal paste is not feasible.
Cons:
- Generally less effective in terms of heat dissipation compared to thermal paste.
- Limited options in terms of thickness and customization.
- May not be suitable for high-performance systems or overclocking.
Frequently asked questions
1. What is the recommended method for removing old thermal paste?
Use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth to gently wipe off the old thermal paste from the CPU and cooler surfaces.
2. How often should I clean and reapply thermal paste?
It is recommended to clean and reapply thermal paste whenever you remove the CPU cooler or notice high temperatures during operation. Generally, every 1-2 years is a good timeframe.
3. Can I reuse thermal paste after removing the cooler?
It is generally not recommended to reuse thermal paste once it has been removed. Fresh thermal paste ensures optimal heat transfer and performance.
4. What precautions should I take when applying thermal paste?
Avoid using excessive amounts of thermal paste, as it can lead to poor heat transfer. Ensure a clean and dry surface before application.
5. How can I ensure proper care for my motherboard?
Ensure proper grounding and handle the motherboard with care to avoid electrostatic discharge. Regularly clean the motherboard from dust and debris using compressed air or a soft brush.
Conclusion
Yes, thermal paste can potentially damage the motherboard if applied improperly or if it seeps into sensitive components. However, as long as you apply the paste correctly and in the recommended amount, the risk of damage is minimal. Just remember to be cautious and follow proper application techniques to ensure the safety of your motherboard.



