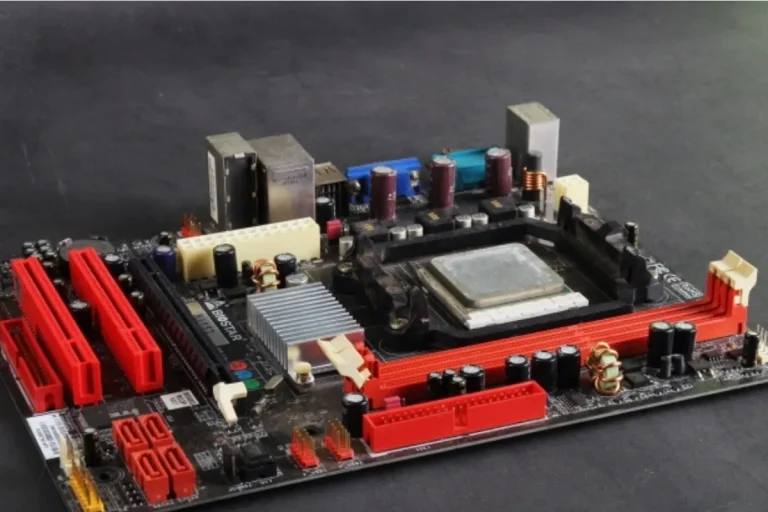
How does a motherboard affect performance?
When it comes to your computer’s performance, the motherboard is the unsung hero that quietly pulls all the strings. It’s like the conductor of an orchestra, ensuring that all the components work together harmoniously. But how exactly does it impact your computer’s speed and efficiency?
Components of a Motherboard
The motherboard is like the backbone of your computer, holding all the essential components together and ensuring they work seamlessly. To understand how a motherboard affects performance, let’s take a closer look at its key components and their roles:
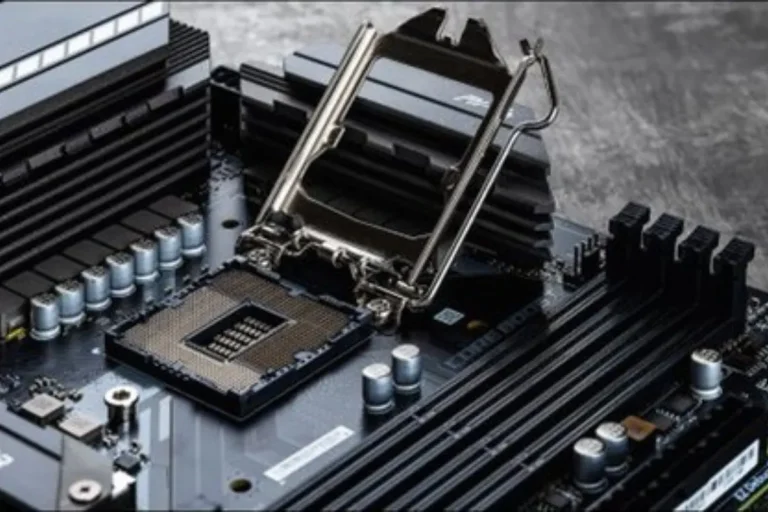
CPU Socket
The CPU socket, also known as the processor socket, is where the brain of your computer, the central processing unit (CPU), is installed. It acts as a bridge between the CPU and the motherboard, allowing data and instructions to flow smoothly. The type of socket determines the compatibility of the CPU, so it’s crucial to choose a motherboard with the right socket for your processor.
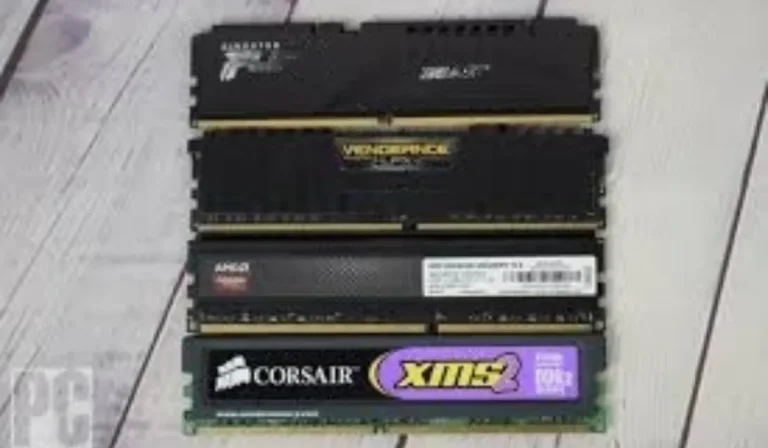
RAM Slots
Random Access Memory (RAM) is your computer’s short-term memory, and the RAM slots on the motherboard hold the memory modules. The more RAM slots available, the more memory you can install, which directly impacts your computer’s multitasking capability and overall speed. It’s essential to check the maximum RAM capacity and supported speed when choosing a motherboard.
Expansion Slots
Expansion slots provide room for additional components to enhance your computer’s functionality. Graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards are commonly inserted into these slots.
The number and type of expansion slots determine the range of upgrades and peripherals you can add to your system. Choosing a motherboard with enough expansion slots ensures future flexibility and compatibility.
Form Factor and Size
When it comes to choosing a motherboard, one important aspect to consider is its form factor and size. The form factor determines the physical dimensions and layout of the motherboard, which in turn affects its performance, flexibility, and compatibility with other components. Let’s dive deeper into the different form factors and their pros and cons:
Explanation of Different Form Factors
There are three common form factors: ATX, microATX, and mini-ITX. ATX is the standard form factor, offering a good balance between performance and expandability. It is larger in size and provides ample room for expansion slots and connectors.
MicroATX is a smaller form factor that sacrifices some expansion options but still offers decent performance and flexibility. Mini-ITX is the smallest form factor, designed for compact and space-constrained systems, but with limited expansion options.
Impact on Performance and Flexibility
The form factor of a motherboard can impact its performance and flexibility. Larger form factors like ATX often offer more expansion slots, allowing for additional components such as dedicated graphics cards or sound cards.
This can enhance gaming or multimedia experiences. However, if you have limited space or require a compact system, a smaller form factor like microATX or mini-ITX may be more suitable. These smaller form factors can still deliver good performance but with fewer expansion options.
Pros and Cons of Each Form Factor
ATX offers the most features and expansion options, making it ideal for high-end systems or those requiring extensive customization. However, its larger size may not fit in all cases. MicroATX strikes a balance between size and features, making it suitable for most mid-range systems.
It offers decent expandability while being more compact than ATX. On the other hand, mini-ITX is the smallest form factor, perfect for compact builds or HTPCs (Home Theater PCs), but with limited expansion options.
Chipset and Bus Speed
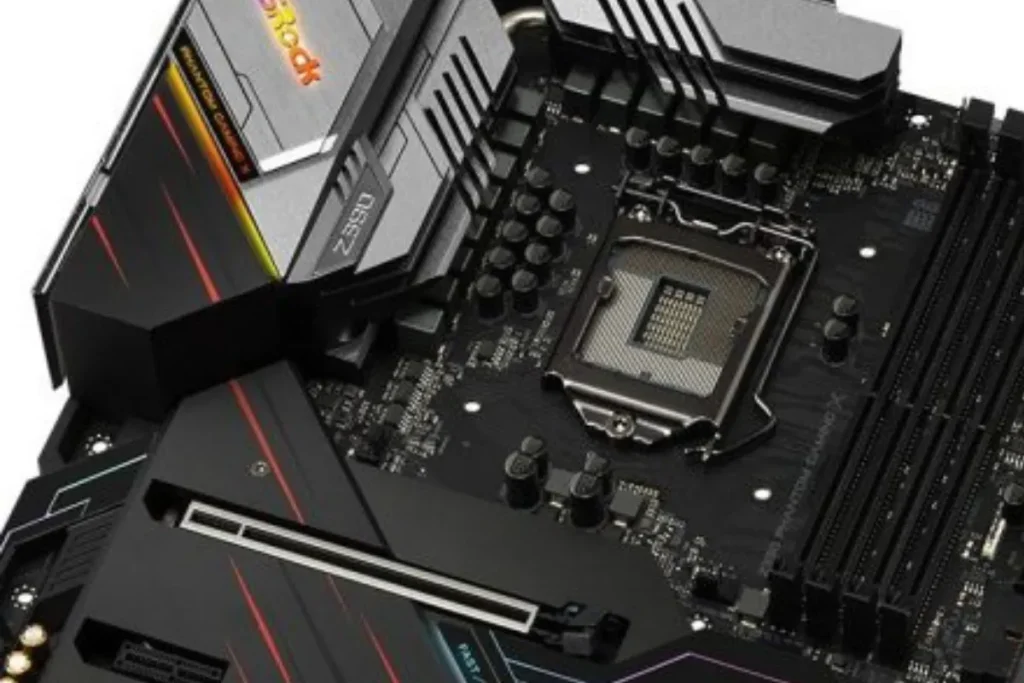

When it comes to understanding the inner workings of a motherboard, two important aspects to consider are the chipset and bus speed. These elements play a significant role in determining the performance and efficiency of your computer system. Let’s explore them in more detail:
Description of the Motherboard Chipset
The chipset is a crucial component that serves as the communication hub between the CPU, memory, storage devices, and other peripherals. It determines the capabilities and features of the motherboard.
The chipset manages data flow, controls input/output operations, and handles the interaction between different hardware components. It has a direct impact on system performance and compatibility with various technologies.
Impact on Performance
The chipset greatly influences the performance of your computer system. It dictates the maximum supported RAM capacity, the number of USB ports, the type and speed of storage interfaces, and the overall stability of the system.
A high-end chipset can support faster data transfer rates, enabling smoother multitasking, faster boot times, and quicker application loading. On the other hand, a lower-end chipset might limit your system’s capabilities and hinder its overall performance.
Importance of Bus Speed
Bus speed refers to the speed at which data travels between the CPU and other components, such as the RAM, graphics card, and storage devices. It plays a crucial role in determining the overall system performance.
A higher bus speed allows for faster data transfer, reducing bottlenecks and enhancing the responsiveness of your computer. The bus speed is closely tied to the CPU’s performance, as it determines how quickly the processor can access and process data.
Frequently asked questions
1. What are PCIe and M.2 expansion slots, and how do they impact performance?
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) and M.2 are types of expansion slots found on motherboards.
2. Why are connectivity options like USB, SATA, and Ethernet important for system performance?
Connectivity options like USB, SATA, and Ethernet play a crucial role in system performance. USB ports allow for the connection of external devices, such as keyboards, mice, and printers.
3. Can I use a PCIe device in an M.2 slot or vice versa?
No, PCIe devices and M.2 devices are not interchangeable. PCIe devices require a PCIe slot, while M.2 devices require an M.2 slot.
4. What is the maximum number of devices I can connect to USB ports?
The maximum number of devices you can connect to USB ports depends on the number of available USB ports on your motherboard and the power requirements of the connected devices.
5. How does the speed of Ethernet ports affect internet connectivity?
The speed of Ethernet ports directly impacts the internet connectivity of your system. Ethernet ports come in different speeds, such as 10/100 Mbps (megabits per second) or 1 Gbps (gigabits per second).
Conclusion
the motherboard plays a vital role in determining the performance of your computer system. It acts as the central hub, connecting all the components together. A well-chosen motherboard with compatible components can enhance speed, responsiveness, and overall efficiency.
So, when it comes to maximizing your system’s performance, don’t underestimate the power of a good motherboard!