Is a motherboard a part of a CPU?
Are you wondering if a motherboard is a part of a CPU? Well, let’s clear up the confusion! A motherboard and a CPU are two essential components of a computer system, but they serve different purposes. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of computer hardware and explore the relationship between these two crucial elements.
Relationship between a Motherboard and CPU
When it comes to understanding how a computer functions, it’s important to grasp the relationship between a motherboard and a CPU. These two components work hand in hand to power your computer system.
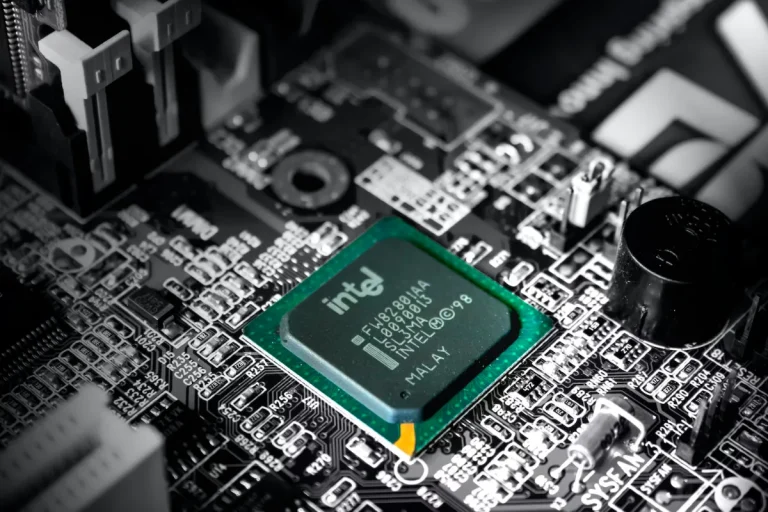
The motherboard acts as the central hub of your computer, connecting all the different components together. It provides a platform for the CPU to reside on and facilitates communication between various hardware components.
Think of the motherboard as the backbone of your computer, enabling everything to work together seamlessly. The CPU, on the other hand, is often referred to as the brain of the computer.
It’s responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations that drive the system’s operations. The CPU relies on the motherboard to provide it with power and a pathway for data transfer.
One crucial aspect of the motherboard-CPU relationship is socket compatibility. The CPU is placed into a specific socket on the motherboard, ensuring a secure connection. Different CPU models require specific socket types, so it’s essential to choose a motherboard that supports your desired CPU.
Additionally, chipset compatibility is another factor to consider. The chipset acts as a bridge between the CPU and the other components on the motherboard. It determines the features and capabilities of the motherboard, such as the number of USB ports, expansion slots, and supported memory types.
Matching the chipset of the motherboard with the CPU ensures optimal performance and compatibility.
The Functionality of a Motherboard

When it comes to the inner workings of a computer, understanding the functionality of a motherboard is essential. The motherboard plays a crucial role in supporting the CPU and ensuring the smooth operation of your computer system.
The motherboard serves as a foundation for all the hardware components in your computer. One of its primary roles is to support the CPU, the central processing unit. The CPU is mounted on the motherboard and relies on it for power and communication with other components.
Power delivery is a critical function of the motherboard. It receives power from the power supply unit and distributes it to various components, including the CPU. This ensures that all the components receive the necessary power to function properly.
Another vital aspect of the motherboard’s functionality is data transfer. It provides pathways for data to flow between different components, such as the CPU, memory, storage devices, and peripherals. The motherboard incorporates various interfaces and connectors to facilitate fast and efficient data transfer.
Expansion slots are also an integral part of the motherboard’s functionality. These slots allow you to expand your computer’s capabilities by adding additional hardware components, such as graphics cards, sound cards, or network cards. Expansion slots provide the necessary connectivity and bandwidth for these components to work seamlessly with the rest of the system.
The Functionality of a CPU
The CPU, or central processing unit, is the powerhouse behind the operation of a computer. Understanding the functionality of a CPU is crucial to comprehend how a computer processes information and performs tasks.
The primary role of the CPU is to process instructions and carry out calculations. It acts as the brain of the computer, executing tasks and controlling the overall operation of the system. Every action you perform on your computer involves the CPU processing instructions to accomplish the desired outcome.
One important aspect of a CPU is the number of cores it possesses. Cores can be thought of as individual processing units within the CPU. A CPU with multiple cores can handle multiple tasks simultaneously, improving overall performance and multitasking capabilities.
Clock speed is another crucial factor in CPU functionality. It refers to the speed at which the CPU can execute instructions. A higher clock speed means that the CPU can process instructions more quickly, resulting in faster overall performance.
Cache memory is a small, high-speed memory storage located on the CPU. It serves as a temporary storage area for frequently accessed data, allowing the CPU to retrieve information quickly. Cache memory helps reduce the time it takes for the CPU to access data from the main memory, enhancing overall processing speed.
Frequently asked questions
1. What are the different form factors for motherboards?
Motherboards come in various form factors, including ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. ATX is the most common form factor, offering ample expansion slots and features. Micro-ATX is smaller but still provides a decent number of expansion options.
2. What are the differences between ATX and Micro-ATX motherboards?
The main difference lies in their size and number of expansion slots. ATX motherboards are larger and typically offer more slots for adding components like graphics cards, sound cards, and additional storage.
3. What is the significance of different CPU generations?
CPU generations indicate the technological advancements and improvements made by manufacturers over time. Each new generation typically offers increased performance, efficiency, and additional features.
4. What are the different types of CPUs available in the market?
CPUs can be categorized into various types, including Intel Core processors, AMD Ryzen processors, and server-grade CPUs. Intel Core processors are popular for desktop and consumer use, while AMD Ryzen processors offer competitive performance and value.
5. What are the key differences between Intel and AMD CPUs?
Intel and AMD CPUs differ in their architecture, performance, and price points. Intel CPUs often excel in single-threaded tasks and gaming, while AMD CPUs offer better multitasking capabilities and value for money.
Conclusion
The motherboard and CPU are two separate components that work together to make your computer function. The motherboard serves as a foundation, connecting various hardware components, while the CPU acts as the brain, processing instructions and carrying out tasks. They are like a dynamic duo, each with its own important role in the grand scheme of your computer system.