What does a motherboard look like?
Are you curious about the inner workings of a computer? Well, let’s take a peek inside and explore the fascinating world of motherboards! A motherboard is like the backbone of a computer, connecting all the vital components together. It’s the unsung hero that makes everything work harmoniously.
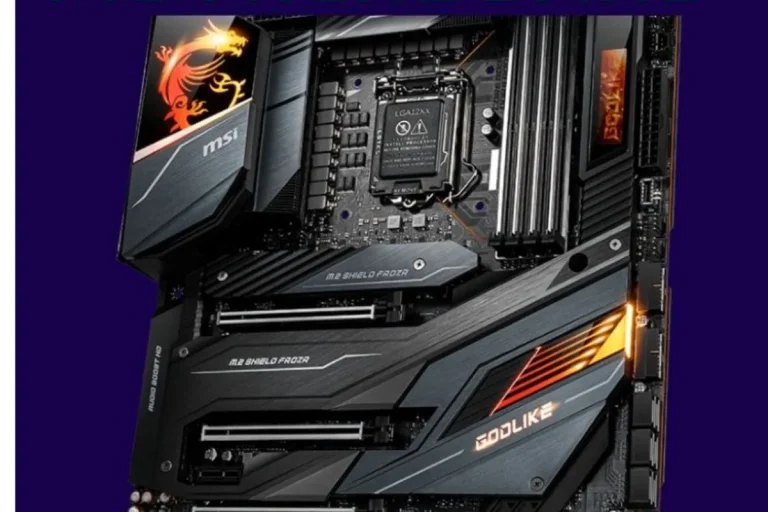
Anatomy of a Motherboard
When it comes to understanding how a motherboard looks and functions, one crucial aspect to consider is its form factor. The form factor refers to the size and layout of the motherboard, which can vary depending on the specific needs and requirements of a computer system.
Form Factor
The form factor determines the physical dimensions of the motherboard and plays a vital role in determining its compatibility with other computer components. There are several popular form factors, including ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX.
- ATX: ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is the most common form factor used in modern desktop computers. It typically measures around 12 x 9.6 inches and offers a good balance between expandability and size.
- Micro-ATX: Micro-ATX is a smaller form factor that measures around 9.6 x 9.6 inches. It is commonly used in compact desktop systems and provides a more space-efficient solution while still offering some expansion options.
- Mini-ITX: Mini-ITX is the smallest form factor, measuring around 6.7 x 6.7 inches. It is ideal for small form factor PCs and is often used in media centers or home theater systems where space is limited.
The form factor of a motherboard affects not only its physical size but also the placement and availability of various connectors and slots. It’s important to choose a motherboard with a compatible form factor to ensure proper fitment within the computer case and compatibility with other components.
Connecting the Brains of Your Computer
The CPU socket is a critical component of a motherboard that plays a crucial role in connecting the processor, also known as the brain of your computer, to the motherboard.
The CPU socket serves as a physical interface that allows the processor to communicate with the rest of the computer system. It provides electrical connections and mechanical support for the processor, ensuring a secure and efficient connection.
There are various types of CPU sockets, each designed to accommodate specific processor models and generations. Some popular CPU socket examples include Intel’s LGA (Land Grid Array) sockets, such as LGA 1151 and LGA 1200, and AMD’s AM4 socket.
Expanding Your Computer’s Memory
When it comes to boosting your computer’s performance, one crucial aspect to consider is the RAM (Random Access Memory). The RAM slots on a motherboard play a vital role in expanding your computer’s memory capacity.
RAM Slots
RAM slots are the physical slots on a motherboard where you install RAM modules. These slots provide the necessary electrical connections to the RAM modules, allowing them to communicate with the processor and store temporary data for quick access.
The number of RAM slots on a motherboard can vary, with most consumer-grade motherboards having two to four slots. Some high-end motherboards can even support up to eight RAM slots, providing ample room for memory expansion.
Expanding Your Possibilities
When it comes to customizing and upgrading your computer, expansion slots are your best friends. These slots, such as PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) and PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect), provide opportunities to add additional components and enhance your computer’s functionality.
Expansion slots serve as connectors on the motherboard that allow you to install various expansion cards, such as graphics cards, sound cards, network adapters, and more. These cards extend the capabilities of your computer, enabling you to enjoy high-quality graphics, immersive audio, and seamless connectivity.
The PCIe slot is the most common and widely used expansion slot today. It offers faster data transfer speeds and improved performance compared to its predecessor, the PCI slot. Graphics cards, in particular, often require a PCIe slot to deliver smooth gaming experiences and handle demanding visual tasks.
Storage Connectors
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a widely used storage connector that supports both hard drives and SSDs. It provides a reliable and efficient connection for transferring data between the storage devices and the motherboard.
SATA connectors are commonly found on motherboards and are backward compatible, allowing you to connect older SATA devices.M.2 is a newer and more compact storage connector that offers faster data transfer speeds compared to SATA.
Power Connectors
Powering your motherboard and its components is essential for a functional computer system. Power connectors are the key to ensuring a steady supply of power to your motherboard, allowing it to run smoothly.
The 24-pin ATX power connector is a primary power connector that provides power to the motherboard itself. It delivers power to various components and ensures stable voltage throughout.
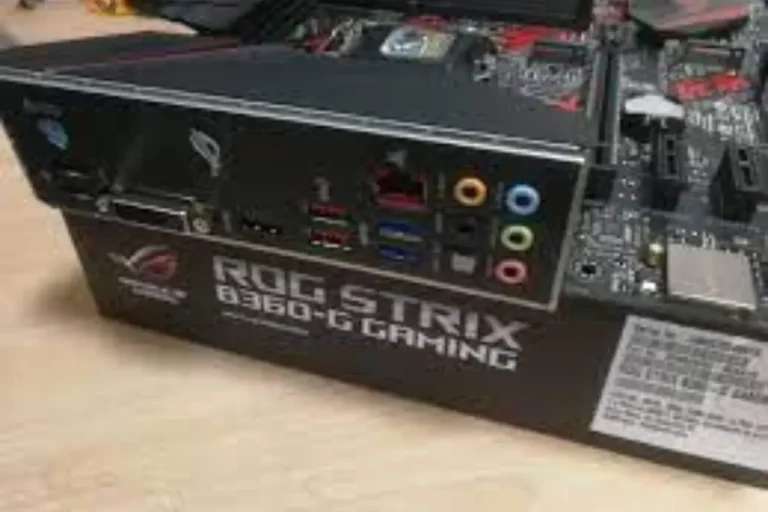
Input/Output Ports
The world of input/output ports is the gateways for connecting external devices to your computer. These ports are typically found on the rear panel of the motherboard, providing convenient access for connecting peripherals.
USB ports are the most common and versatile ports, allowing you to connect a wide range of devices, including keyboards, mice, printers, and external storage devices. HDMI ports enable you to connect your computer to external displays or TVs, delivering high-definition audio and video signals.
Frequently asked question
1. Why is visual representation important in technical content?
Visual representation, such as labeled diagrams and images, enhances understanding by providing a clear and concise visual reference.
2. How do labeled diagrams aid in understanding technical information?
Labeled diagrams provide a visual map that highlights the key components and their connections. This helps readers grasp the spatial relationships and functions of the various elements discussed, facilitating a deeper understanding of the topic at hand.
3. Can images and diagrams be used to simplify complex technical concepts?
Absolutely! Images and diagrams simplify complex concepts by breaking them down into visual elements that are easier to comprehend.
4. What are the benefits of using visual representation in technical documentation?
Visual representation enhances the readability and accessibility of technical documentation. It improves comprehension, reduces the chances of misinterpretation, and helps readers quickly locate and understand the various components being discussed.
5. Where can I find visual representations of the components discussed?
Visual representations, such as labeled diagrams and images, can often be found within the technical content itself. They may be included directly in the article or as supplementary materials, such as downloadable files or links to external resources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a motherboard is like the bustling central hub of a computer, connecting all the vital components that make it work. It looks like a flat, rectangular circuit board with various slots, ports, and connectors.
Think of it as the backbone that brings everything together, ensuring your computer runs smoothly and efficiently. So, next time you peek inside your computer case, remember that the motherboard is the unsung hero that keeps everything connected and humming along.