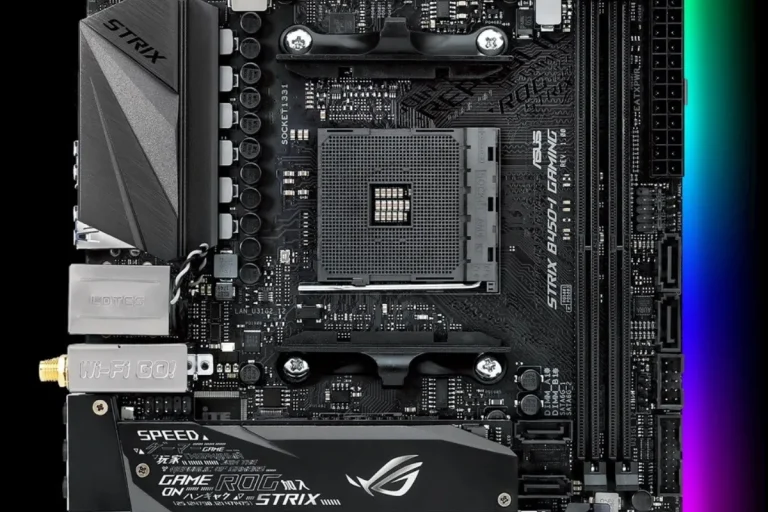
What is a heat sink on a motherboard?
A heat sink on a motherboard is like a superhero cape for your computer, swooping in to save the day by keeping things cool. It’s a crucial component that helps dissipate heat from important parts, preventing overheating and potential damage.
The Role of Heat Sink in a Motherboard
When it comes to your computer’s motherboard, there’s a lot happening under the hood. All those tiny components working together can generate a surprising amount of heat. That’s where the heat sink steps in, playing a crucial role in keeping things cool and preventing potential damage.
The motherboard’s components and their heat
A motherboard is like the central nervous system of your computer, connecting all the different parts and allowing them to communicate. However as these components work hard to process information and perform tasks, they can generate heat as a byproduct.
The CPU (central processing unit), chipset, and VRM (voltage regulator module) are some of the main culprits when it comes to heat generation.
Dissipate heat from critical components
Enter the heat sink, the unsung hero that tackles the heat issue head-on. A heat sink is a specially designed metal structure that attaches to these critical components on the motherboard.
Its primary function is to absorb and dissipate the excess heat generated by these components, ensuring they operate within safe temperature limits. The heat sink achieves this through a combination of clever design and materials.
Its fins provide a larger surface area for heat to spread, while the base and heat pipes efficiently transfer the heat away from the component. Additionally, a thermal interface material is applied between the heat sink and the component to optimize heat transfer.
Importance of proper installation and maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance of the heat sink are essential for its optimal performance. Ensuring a secure and snug fit of the heat sink on the component helps maximize heat transfer.
Regular cleaning of the heat sink to remove dust and debris is also important to prevent any obstruction that could hinder its effectiveness.
Types of Heat Sinks on Motherboards
When it comes to heat sinks on motherboards, it’s not a one-size-fits-all situation. Different components require specific types of heat sinks to effectively dissipate heat and maintain optimal temperatures. Let’s explore the common types of heat sinks found on motherboards and understand their purpose and functionality.
Overview of common heat sinks found on motherboards
Motherboards host a variety of components that generate heat, and each of these components may require a dedicated heat sink. The most commonly seen heat sinks on motherboards include those for the CPU (central processing unit), chipset, and VRM (voltage regulator module). Each of these heat sinks serves a specific purpose in managing heat.
Explanation of each purpose and functionality
The CPU heat sink is perhaps the most important one. It sits atop the CPU and helps dissipate the heat generated by the processor. The chipset heat sink, on the other hand, focuses on cooling the chipset, which handles data flow between various components. Lastly, the VRM heat sink is responsible for cooling the voltage regulator module, which ensures stable power delivery to the CPU.
a heat sink for a specific component
When selecting a heat sink, several factors come into play. Firstly, compatibility with the specific component is crucial. The heat sink should be designed to fit the component perfectly.
Additionally, factors such as heat dissipation capacity, noise level, and overall thermal performance should be considered to ensure optimal cooling.
Heat Sink Design and Materials

When it comes to heat sink design and materials, there are various options to consider. The design and material of a heat sink play a crucial role in its effectiveness at dissipating heat from critical components.
Explanation of different heat sink designs
Heat sinks come in different shapes and sizes, each with its own design and purpose. Tower heat sinks, as the name suggests, resemble vertical towers and are often used for CPUs. They feature multiple heat pipes and fins to efficiently transfer heat away from the component.
Down-blowing and top-blowing heat sinks are designed to direct airflow towards the motherboard. Down-blowing heat sinks blow air directly onto the component while top-blowing heat sinks blow air over the component.
Overview of commonly used heat sink materials
Heat sinks are typically made from either aluminum or copper, with each material offering unique characteristics. Aluminum heat sinks are lightweight, affordable, and have good thermal conductivity.
Copper heat sinks, on the other hand, have excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer. However, copper heat sinks tend to be heavier and more expensive than their aluminum counterparts.
Pros and cons of different designs and materials
Tower heat sinks provide excellent cooling performance and are ideal for high-performance CPUs. Down-blowing and top-blowing heat sinks are effective in ensuring airflow over the motherboard, but they may not provide as much cooling performance as tower heat sinks.
Aluminum heat sinks are cost-effective and lightweight, while copper heat sinks offer superior thermal conductivity but come at a higher cost.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why should I use a heat sink on my motherboard?
A heat sink helps dissipate heat generated by critical components, such as CPUs or chipsets, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
2. How does a heat sink improve system performance?
By efficiently transferring heat away from components, a heat sink keeps them within safe operating temperatures. This allows them to perform at their best, avoiding thermal throttling and maintaining consistent performance levels.
3. Can a heat sink extend the longevity of my components?
Absolutely! Excessive heat can shorten the lifespan of electronic components. By keeping temperatures in check, a heat sink helps prevent premature aging and potential failures, thus extending the longevity of your components.
4. What happens if I don’t use a heat sink on my motherboard?
Without a heat sink, components can quickly overheat, leading to reduced performance, system instability, and potential damage or failure of the component. It is highly recommended to use a heat sink to prevent these issues.
5. Are all heat sinks compatible with any motherboard?
Heat sink compatibility depends on factors such as socket type, component size, and motherboard layout. It’s important to choose a heat sink that is specifically designed for your motherboard and compatible with the component you’re cooling.
Conclusion
A heat sink on a motherboard is a crucial component that helps dissipate heat, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating. By efficiently transferring heat away from critical components like CPUs or chipsets, it improves system longevity and prevents potential failures. So, remember, a heat sink is your motherboard’s best friend in keeping things cool and running smoothly