Why is the LAN port on my motherboard not working?
Is your motherboard’s LAN port giving you a hard time? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll explore the reasons behind a non-working LAN port and provide simple troubleshooting steps to help you get back online.
Common Causes of LAN Port Issues
Are you experiencing trouble with your LAN port? Several common causes can lead to connectivity problems. Let’s explore each of them in detail:
Physical damage or loose connections
Sometimes, physical damage or loose connections can hinder the proper functioning of your LAN port. A bent or broken Ethernet cable, a damaged LAN port on your motherboard, or loose connections can all contribute to the issue. Check the physical condition of your cables and ensure they are securely plugged in.
Outdated or incompatible drivers
Outdated or incompatible LAN drivers can also be a culprit. Drivers are software that allows your operating system to communicate with hardware devices.
If your LAN drivers are outdated or incompatible with your motherboard, it can result in a non-working LAN port. Updating the drivers to the latest version can often resolve this issue.
Network adapter settings or configuration issues
Misconfigured network adapter settings can interfere with the proper functioning of your LAN port. Incorrect settings such as IP address conflicts or incorrect DNS settings can prevent your computer from connecting to the network. Double-checking and adjusting these settings can help resolve the problem.
Troubleshooting Steps
Is your LAN port still giving you trouble? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered with some simple troubleshooting steps.
Checking physical connections and cables
Start by examining the physical connections and cables associated with your LAN port. Ensure that the Ethernet cable is securely plugged into both the LAN port on your motherboard and the router or modem.
Additionally, check for any visible damage to the cable or port. Replacing a faulty cable or fixing loose connections can often resolve the issue.
Updating LAN drivers and firmware
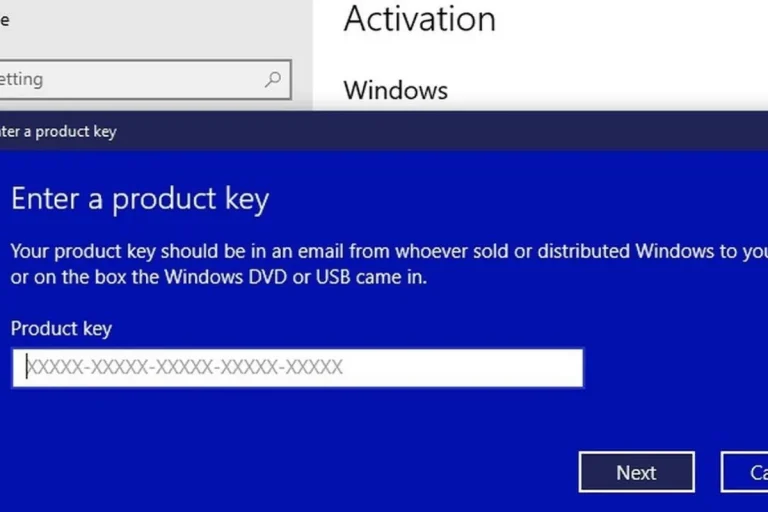
Outdated LAN drivers or firmware can lead to connectivity problems. Visit the manufacturer’s website and download the latest LAN drivers for your motherboard model.
Install the updated drivers and firmware to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. This simple step can make a big difference in resolving LAN port issues.
Verifying network adapter settings
Double-check your network adapter settings to ensure they are correctly configured. Go to the Network and Sharing Center in your operating system and review the settings for your LAN connection.
Verify that the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server settings are correct. Adjust any incorrect settings to align with your network’s requirements.
Advanced Troubleshooting

If you’re still facing issues with your LAN port, it’s time to dive into advanced troubleshooting techniques. Let’s explore some additional steps you can take to get your LAN port up and running smoothly again.
Exploring BIOS settings related to LAN functionality
Access your computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) settings and explore options related to LAN functionality. Look for settings such as LAN controller enable/disable or LAN boot priority.
Ensure that the necessary LAN-related settings are enabled and configured correctly. Making the appropriate changes in the BIOS can help resolve stubborn LAN port issues.
Disabling power-saving features that may affect the LAN port
Certain power-saving features in your operating system may affect the performance of your LAN port. To rule out this possibility, navigate to your power settings and disable any power-saving features specifically related to the LAN adapter.
By keeping the LAN port active at all times, you can prevent any disruptions caused by power-saving settings.
Resetting BIOS to default settings
If all else fails, resetting your computer’s BIOS to default settings can help resolve persistent LAN port issues. This action will revert any changes you have made in the BIOS to the original factory settings.
Consult your motherboard’s manual or the manufacturer’s website for instructions on how to perform a BIOS reset. Remember to back up any important data before proceeding with this step.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the indications of a hardware failure?
Indications of a hardware failure can include system crashes, error messages, random restarts, or components not functioning properly.
2. When should I contact the manufacturer or a professional technician?
It is advisable to contact the manufacturer or a professional technician if you have tried basic troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing persistent issues with your hardware.
3. What should I consider when exploring warranty options?
When exploring warranty options, consider the duration of the warranty, what it covers (parts, labor, shipping), any additional costs or conditions, and the reputation and reliability of the manufacturer or service provider.
4. How can I find reliable repair services for my hardware?
To find reliable repair services, you can start by checking reviews and ratings online, asking for recommendations from friends or colleagues, or contacting the manufacturer for authorized service centers.
5. Should I repair or replace my hardware?
The decision to repair or replace your hardware depends on various factors, such as the cost of repairs compared to the cost of a new device, the age and overall condition of the hardware, and your personal preferences.
Conclusion
if you’re experiencing issues with your LAN port on the motherboard, don’t panic. By following the troubleshooting steps we’ve discussed, such as checking physical connections, updating drivers, and exploring advanced settings, you can often resolve the problem.
Remember to be patient and thorough in your troubleshooting process, and don’t hesitate to seek professional help if needed.